Capturing Carbon With Waste And Waste Heat
Advanced Renewable
Mon , 13 May 2024 21:56 WIB

Carbon capture is still an expensive solution to rid the earth's atmosphere of contaminated CO2 emissions, therefore many chimneys from power plants and industry are still allowed to rapidly release CO2 emissions into the sky.
To accelerate decarbonization, at least two things are needed. The first is the low cost of carbon capture and the use of high-value catches. If these two things are fulfilled, carbon capture and utilization (CCU) activities will no longer be a cost center for industry, CCU can even become a profit center.
When CCU becomes a profit center, industry will naturally want to do this CCU and the reduction in CO2 emissions can accelerate quickly. There are two ways to capture carbon which, according to the results of our study, can be done at low cost.
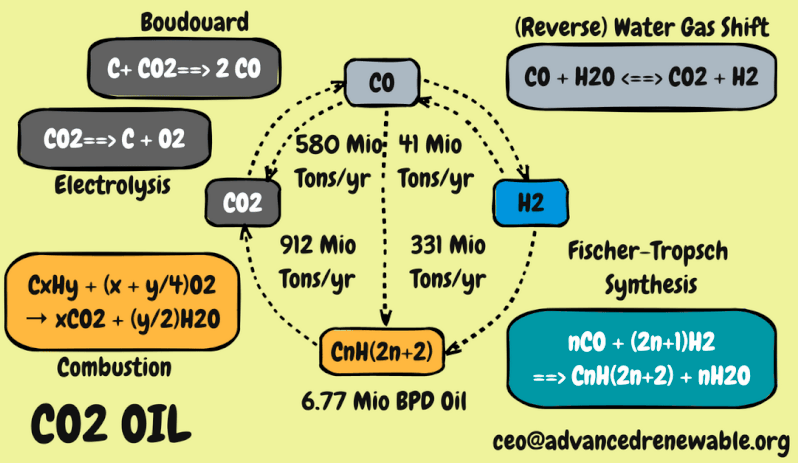
Firstly, using carbon from the carbonization of waste, because carbon or charcoal from this waste is cheap, and it only takes around 270 grams of charcoal to capture 1 kg of CO2, so the cost of capturing CO2 this way will be cheap. Second, using hydrogen, hydrogen which is generally expensive, can be produced cheaply if electricity for electrolysis is obtained cheaply or even for free, and this is possible if the source of electrical energy comes from the use of waste heat. The two chemical reactions below are this low cost carbon capture process.
The two methods of capturing CO2 with carbon and with H2 both produce CO gas, which is the main component of syngas. Syngas is a cheap energy product because it has low calories. However, from this CO gas, all forms of fuel that we use can be produced, such as diesel, gasoline, LPG and even to produce more hydrogen.
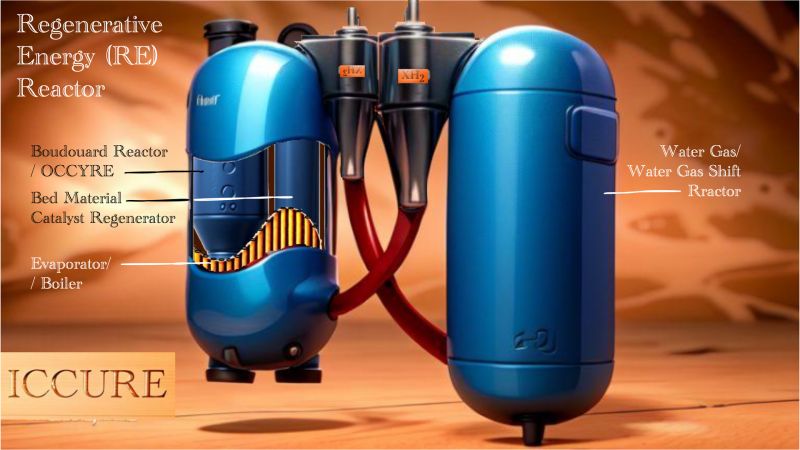
There are 3 reactors needed for the CCU program - carbon capture and its use into high-value products. Firstly the OCCYRE (Onboard Carbon Cycle for Regenerative Energy) reactor to facilitate the Boudouard reaction. The two XH2 (Extra High Hydrogen) reactors are for the Reverse Water Gas Shift (RWGS) reaction, or reversing the direction of the Water Gas Shift (WGS) reaction. And the three GTX reactors, to convert CO and H2 gas in the right ratio into the hydrocarbon fuel mentioned above.
Starting from the two reactions of Boudouard and RWGS, CO2 emissions, which have been the scapegoat for global warming, climate change, extreme weather and various disaster after disaster, should now be able to be handled quickly, structured, systematically and massively, through CO2 capture with waste and waste heat, this could become its own profit center for industries that want to start doing it.
Pos Lainnya
Penampakan Regenerative Energy Reactor
May 13, 2024
Melepas Belenggu Crude Oil Menuju Bio-Oil
May 13, 2024
Regenerative Energy Ecosystem
May 13, 2024
Distributed Fuels Production and Power Generation
May 13, 2024
Introducing the New Oil : CO2 Oil
May 13, 2024
Kategori
Renewable Energy





Silakan mendaftar terlebih dahulu!
Untuk memposting komentar baru. Anda harus login terlebih dahulu. Masuk
Komentar
Tidak ada komentar